Mezzanines—intermediate floors within existing structures—are critical for maximizing space in industrial, commercial, and logistics settings.
Hot-rolled steel(HR) is produced by heating steel billets to extremely high temperatures (typically 1,000–1,200°C, above the metal’s recrystallization point) and rolling them into standardized shapes—such as I-beams, channels, angles, and plates.
HR is a versatile and cost-effective material widely used in mezzanine construction due to its strength, durability, and ease of fabrication.
Below is a detailed analysis of its advantages, applications, and key considerations for mezzanine design.
1. Why Hot-Rolled Steel for Mezzanines?
Mezzanines require materials that balance strength, weight, flexibility, and longevity. Hot-rolled steel excels in all these areas, addressing the core demands of mezzanine design.
(a) Structural Strength & Load Capacity
Hot-rolled steel (e.g., Q235, Q355) offers high yield strength (235–355 MPa) and tensile strength, making it ideal for supporting heavy loads in industrial and commercial mezzanines.
The hot-rolling process relieves internal stresses, making the steel flexible and resistant to brittle failure.
Compared to cold-formed steel, hot-rolled sections (like H-beams) provide greater rigidity and resistance to deflection under dynamic loads (e.g., warehouse pallet racks).
(b) Cost Efficiency & Fabrication Flexibility
Lower production costs than cold-rolled steel due to simplified manufacturing (direct rolling at high temperatures) .
Mass production of standardized shapes reduces manufacturing costs compared to custom-formed metals.
Easily welded, cut, and bolted, allowing for modular mezzanine designs that can be adjusted or expanded.
(c) Fire Resistance & Longevity
Performs better in fire conditions compared to wood or light-gauge steel, especially when paired with intumescent coatings.
Resistant to corrosion when galvanized or painted, extending service life in humid environments.
2. Key Applications in Mezzanine Construction
3. Design Considerations
(a) Material Selection
For heavy-duty mezzanines: Use S355JR/S355ML steel (higher toughness for seismic zones) .
For corrosive environments: Opt for galvanized hot-rolled steel or apply protective coatings.
(b) Connection Methods
Bolted connections: Preferred for modular mezzanines requiring future reconfiguration.
Welded joints: Provide rigidity but require skilled labor and post-weld inspections.
(c) Compliance & Standards
Ensure adherence to EN 1993-1-1 (Eurocode 3) or AISC 360 for structural design.
Fireproofing requirements may apply (e.g., EN 13381-4 for steel protection systems).
4. Case Study: Industrial Mezzanine with Hot-Rolled Steel
Project: A 1,200 m² warehouse mezzanine in Germany used HEB 300 beams and S355JR columns, supporting 5 kN/m² live loads.
Outcome: 30% faster installation vs. cold-formed steel, with 15% cost savings on material procurement.
5. Future Trends
Hybrid systems: Combining hot-rolled steel frames with lightweight composite decks (e.g., steel-concrete) for optimized weight-to-strength ratios.
Automated fabrication: CNC-cut hot-rolled sections reducing on-site labor (e.g., Atomat Spa’s CNC machining).
Why Hot-Rolled Over Alternatives?
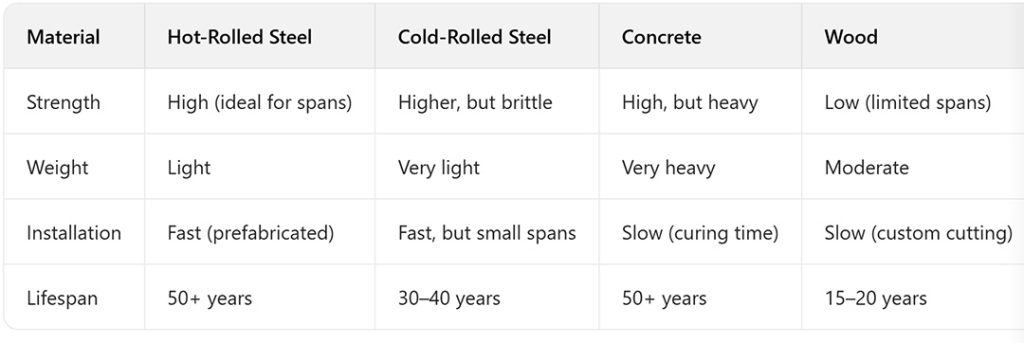
Conclusion
HR is a versatile and cost-effective material, is the go-to choice for mezzanine construction due to its strength, durability, and ease of fabrication.
For specialized needs (e.g., seismic resilience or extreme loads), consult engineers to select the optimal grade and connection design.







